R.C.D. Mallorca vs. RCD Espanyol: La Liga Clash – Game Preview & Predictions
Potential Outcomes and Predictions
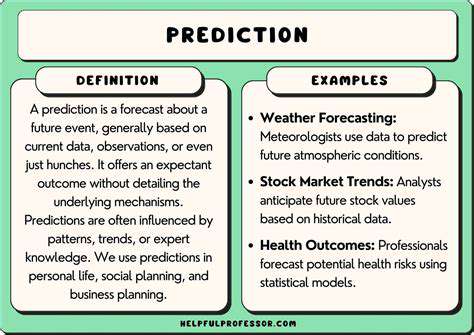
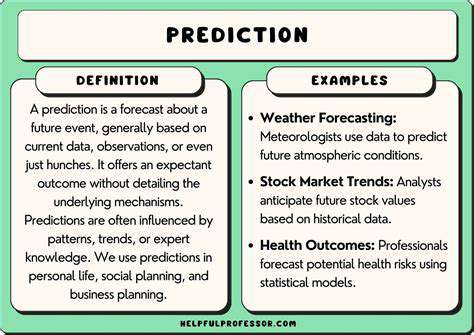
Potential Economic Impacts
Analyzing the potential economic impacts of a new technology is crucial for investment decisions and policy formulation. A successful rollout could lead to significant job creation in related sectors, boosting economic growth and potentially lowering consumer prices. However, there's also the risk of displacement in existing industries, requiring workforce retraining and adaptation strategies.
The scale of these impacts will depend heavily on factors such as the rate of adoption, government policies, and the responsiveness of businesses. The initial stages of adoption may experience fluctuations, but long-term trends should become more predictable as the technology matures and its applications become clearer.
Market Share Predictions
Predicting market share is inherently complex, as it hinges on consumer preferences, competitive landscape, and technological advancements. Early adopters and market penetration rates will play a significant role in shaping the trajectory of market share. Factors such as pricing strategies, brand recognition, and the overall quality of the product will all influence the success of the market entry.
Competitor responses and the emergence of disruptive technologies are also significant variables to consider. Rigorous market analysis and forecasting models are essential for developing a comprehensive understanding of potential market share outcomes.
Consumer Behavior Analysis
Understanding consumer behavior is essential to predict the adoption rate and overall impact of new technologies. Consumer willingness to adopt new technologies is influenced by factors like perceived value, ease of use, and social influence. This analysis must consider demographic and psychographic factors, as well as cultural nuances in different regions and countries.
Technological Advancements and Disruptions
Technological advancements often lead to both disruptions and opportunities. The pace of innovation can be unpredictable, leading to shifts in market dynamics and requiring companies to adapt rapidly. Ongoing research and development efforts in related fields can significantly influence the trajectory of the technology's development.
Anticipating these disruptions is vital for strategic planning. Businesses need to be agile and adaptable to navigate the changing landscape and capitalize on new opportunities.
Regulatory and Policy Implications
New technologies often raise complex regulatory and policy questions. Government responses to these emerging technologies will shape their adoption and impact. Regulations and policies can either accelerate or impede the development and deployment of the technology. Balancing innovation with societal concerns is a crucial challenge.
The development of clear regulatory frameworks is essential for fostering trust and enabling responsible innovation. This will also encourage investment and growth, while mitigating potential risks to consumers and society.
Societal and Cultural Impacts
New technologies have far-reaching societal and cultural impacts that are often overlooked in initial assessments. The integration of this technology into daily life will undoubtedly reshape social interactions, communication patterns, and cultural norms. Assessing potential societal impacts is critical for ensuring responsible development and deployment.
It's important to consider the potential for both positive and negative societal consequences, and to develop strategies to address potential challenges. Public discourse and engagement are crucial for a balanced and inclusive approach.
Possible Impact of Factors Beyond the Pitch
Potential Economic Ripple Effects
The global interconnectedness of economies means that events in one region can have significant and far-reaching consequences in others. Economic downturns in major global markets can lead to reduced demand for exports from developing nations, impacting their GDP growth and employment rates. For instance, a sharp decline in consumer confidence in the United States could trigger a reduction in investment and spending, leading to a slowdown in manufacturing and a consequent decrease in demand for raw materials from other countries.
Supply chain disruptions, triggered by geopolitical events or natural disasters, can also create substantial economic ripples. These disruptions can lead to shortages of vital components, impacting production schedules and causing price increases for finished goods, ultimately affecting consumers and businesses worldwide.
Geopolitical Instability and Security Concerns
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts often have profound consequences for international trade and investment. Escalations in conflicts can lead to sanctions, trade restrictions, and disruptions in supply chains, impacting global commerce and potentially leading to a global recession. The uncertainty surrounding these events can also negatively impact investor confidence and hinder economic growth.
Furthermore, the security concerns stemming from these instabilities can cause businesses to relocate operations, leading to job losses in certain regions and potentially altering the global economic landscape.
Technological Advancements and Disruptions
Rapid technological advancements, while often seen as beneficial, can also create unforeseen disruptions. The emergence of new technologies can render existing skills obsolete, leading to job displacement and requiring significant workforce retraining efforts. This can create social and economic inequalities if not managed effectively.
Furthermore, technological advancements can also lead to significant shifts in production processes and supply chains, requiring businesses to adapt and potentially leading to a need for substantial investments in new technologies. These disruptions can create uncertainty and challenge the established economic order.
Environmental Factors and Climate Change
The impact of environmental factors, particularly climate change, on the global economy is becoming increasingly significant. Climate-related disasters, such as floods, droughts, and storms, can cause significant damage to infrastructure and disrupt supply chains. These disruptions can lead to substantial economic losses and hinder economic growth, particularly in vulnerable regions.
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events are placing a greater strain on resources and infrastructure, requiring substantial investments in adaptation and mitigation strategies. This can divert resources away from other sectors, potentially slowing down overall economic growth in the long term.
Social and Demographic Shifts
Changes in social and demographic patterns can also have significant implications for economic growth and development. Aging populations in developed countries can lead to a shrinking workforce and reduced consumption, potentially impacting economic productivity. This can create a need for increased investment in social security systems and healthcare infrastructure.
Demographic shifts in developing countries, such as rapid urbanization and increased youth populations, can create opportunities for economic growth if effectively managed. However, these shifts can also pose challenges, such as providing adequate infrastructure and employment opportunities for the growing population.
Natural Resource Depletion and Scarcity
The depletion of natural resources and the increasing scarcity of certain materials, such as water and minerals, are becoming increasingly critical issues for economic development. The costs of extraction and transportation of these resources are rising, impacting production costs and potentially leading to price increases for consumers. This can exacerbate existing economic inequalities.
The rising demand for natural resources in growing economies can also lead to environmental degradation and conflicts over access to resources, further complicating global economic stability. Sustainable resource management strategies are crucial to mitigating these future risks.
Read more about R.C.D. Mallorca vs. RCD Espanyol: La Liga Clash – Game Preview & Predictions
Hot Recommendations
-
*King Charles III: Royal Legacy, Duties & Modern Challenges
-
*Jennifer Tilly: Hollywood Career, Iconic Roles & Latest Updates
-
*F1 Sprint Race Explained: Format, Tips & Championship Impact
-
*Jay Bilas Bracket: College Basketball Insights and Expert Predictions
-
*New Mexico Travel Guide: Top Destinations, Culture & Hidden Gems
-
*Steve Harvey: Comedian, Talk Show Icon & Latest Ventures
-
*Jerome Baker: NFL Profile, Career Stats & Future Potential
-
*Dallas Stars: NHL Team Profile, Season Recap & Future Projections
-
*When Is the NFL Draft? Complete Guide to Dates, Teams & Insider Analysis
-
*Kyle Gibson: MLB Pitching Spotlight – Stats, Career Recap & Recent Performances